What is Cataract?
A cataract is the clouding of the lens inside the eye, which results in diminished vision. The lens is normally clear and helps to focus light on the retina at the back of the eye. When a cataract forms, the lens becomes opaque or cloudy, which interferes with vision.
Why it matters?
Cataracts commonly develop slowly and can affect daily activities like reading, driving, and recognising faces. They are treatable — most often by surgically replacing the cloudy lens with an intraocular lens (IOL).
Common symptoms
- Blurry or cloudy vision
- Glare and halos around lights
- Colours appear faded or yellowed
- Difficulty driving at night
- Needing brighter light for reading
What are types of Cataract, its causes, symptoms and treatment?
| Types of Cataract | Causes | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary Cataract | Also known as Posterior Capsule Opacification (PCO); can occur after cataract surgery due to thickening of the lens capsule. | Blurry or dim vision, similar to the original cataract symptoms. | Treated with a quick, non-invasive procedure called YAG laser capsulotomy to clear the cloudy capsule. |
| Traumatic Cataract | Result of an injury or trauma to the eye, such as a blow or penetration. | Blurry vision, pain, light sensitivity, and possible visible changes in the eye. | Treatment may involve surgery to remove the cataract and repair any other damage to the eye. |
| Congenital Cataract | Present at birth or develops in early childhood; can be due to genetic factors or in association with other conditions. | Vision problems, often noticed as a child has difficulty seeing clearly; may be detected through a routine eye exam. | Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the cataract, often at an early age to prevent vision impairment. |
| Radiation Cataract | Caused by exposure to radiation, such as during cancer treatment or excessive UV exposure. | Gradual vision loss, similar to other types of cataracts, including blurred vision and light sensitivity. | Treatment usually requires cataract surgery to remove the affected lens and replace it with an artificial lens. |
When to Consult an Ophthalmologist for Cataracts?
| Situation / Symptom | Reason to Consult an Ophthalmologist |
|---|---|
| Blurred or Hazy Vision | Persistent blurriness or haziness in vision that affects daily activities may indicate cataracts and requires evaluation. |
| Difficulty Seeing at Night | If you experience increased difficulty seeing in low light or at night, it could be a sign of cataracts. |
| Sensitivity to Glare | Increased sensitivity to glare from headlights, lamps, or sunlight can be a symptom of cataracts. |
| Seeing Halos Around Lights | Halos or glare around lights, especially at night, can be a result of cataracts and should be assessed by an ophthalmologist. |
| Fading or Yellowing of Colours | A noticeable change in colour perception, such as colours appearing faded or yellowed, may indicate cataract formation. |
| Frequent Changes in Glasses Prescription | If frequent changes in your glasses or contact lens prescription are needed, it may be due to cataracts. |
| Vision Impairment Affecting Daily Life | When cataracts are impairing your ability to perform everyday tasks like reading, driving, or recognising faces. |
Samarth Netralaya’s Recommendations:
Routine Eye Exams
Even if you do not have noticeable symptoms, regular eye exams can help detect cataracts early.
Early Consultation
It allows for timely intervention, which can prevent significant vision loss and improve treatment outcomes.
Different Cataract Surgeries Available at Samarth Netralaya
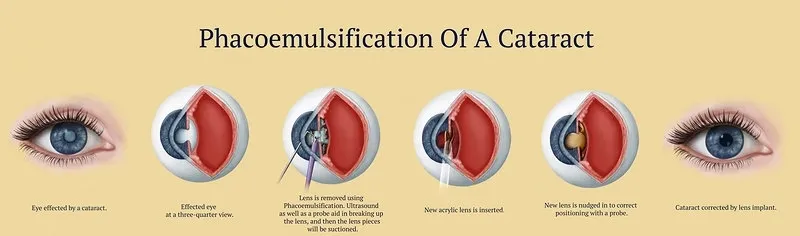
Phacoemulsification (Phaco)
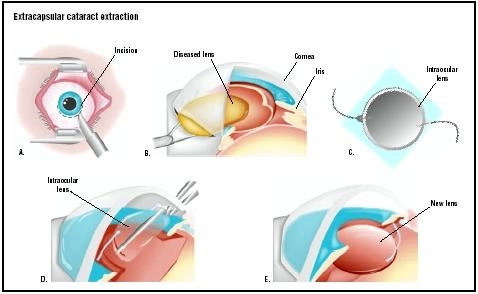
Extracapsular Cataract Extraction (ECCE)
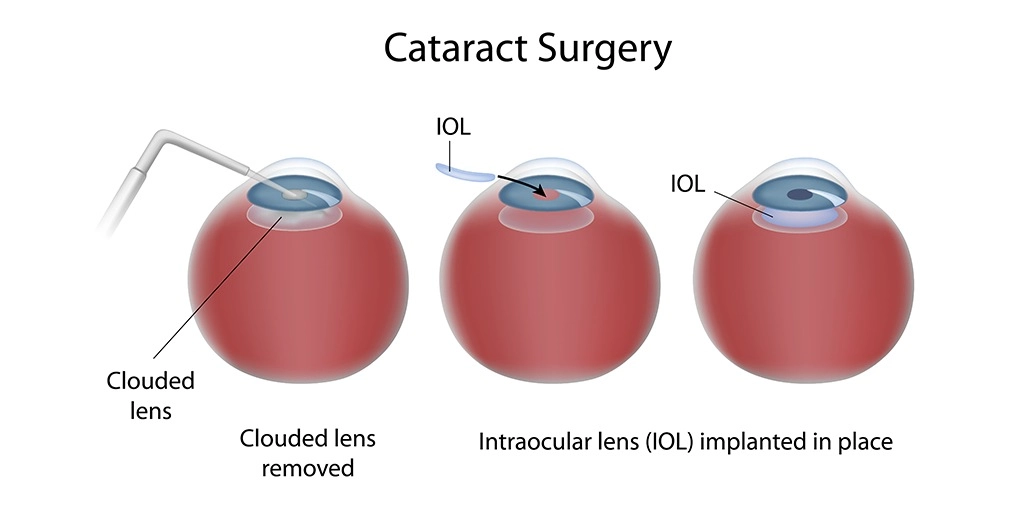
Intracapsular Cataract Extraction (ICCE)
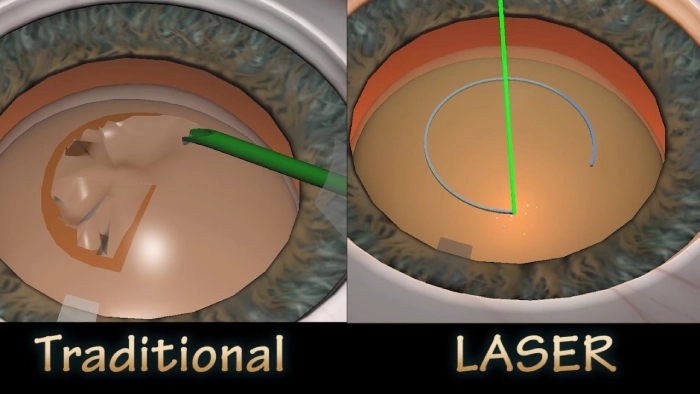
Laser-Assisted Cataract Surgery (FLACS)
